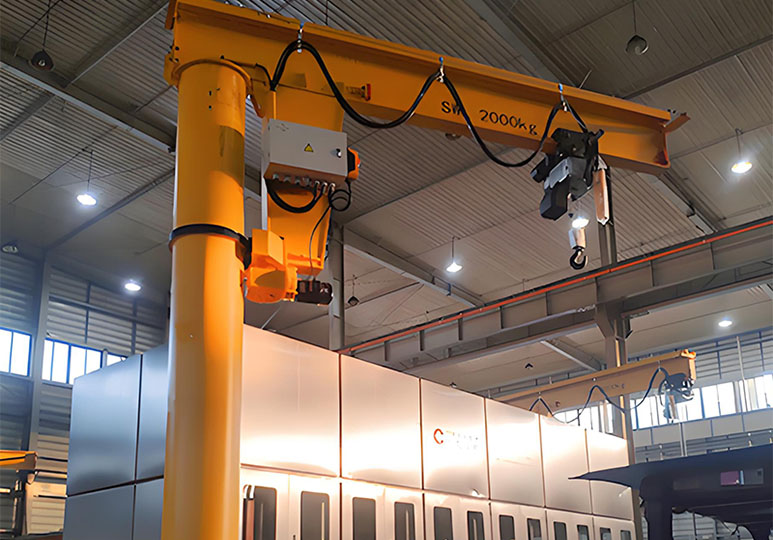
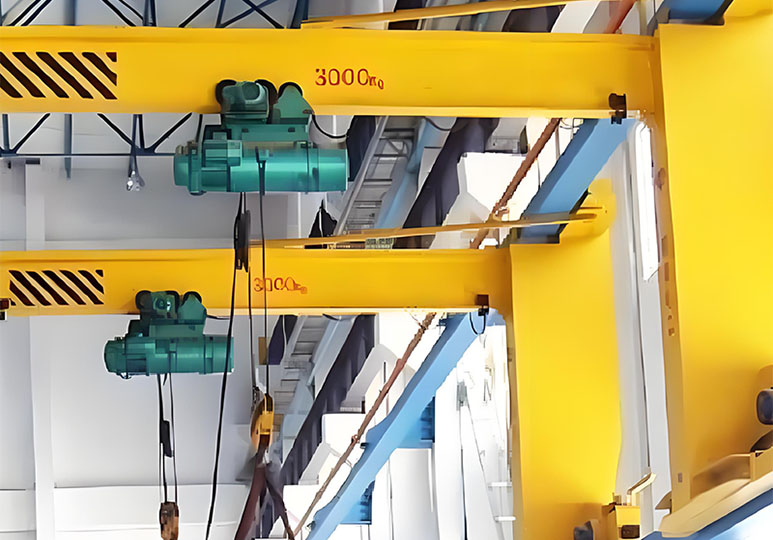
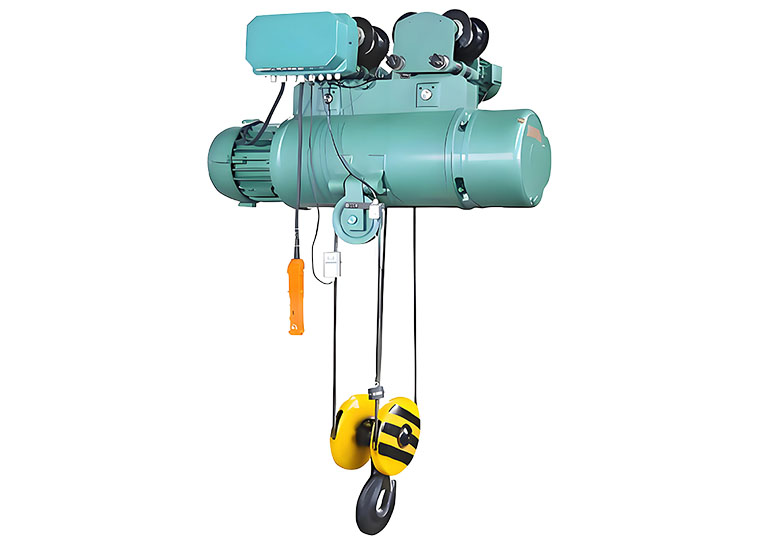
The overhead crane is an indispensable heavy material handling equipment in modern industry. It has a unique structural design and strong load capacity, widely used in manufacturing, construction, warehousing and logistics and other fields. It can efficiently and safely complete the lifting and transportation of heavy materials. In this article, we will discuss the overhead crane system, parts, different types of overhead cranes, and related operation and maintenance points, while providing you with practical advice on buy overhead crane, including how to selecting a quality manufacturer, and customized solutions.
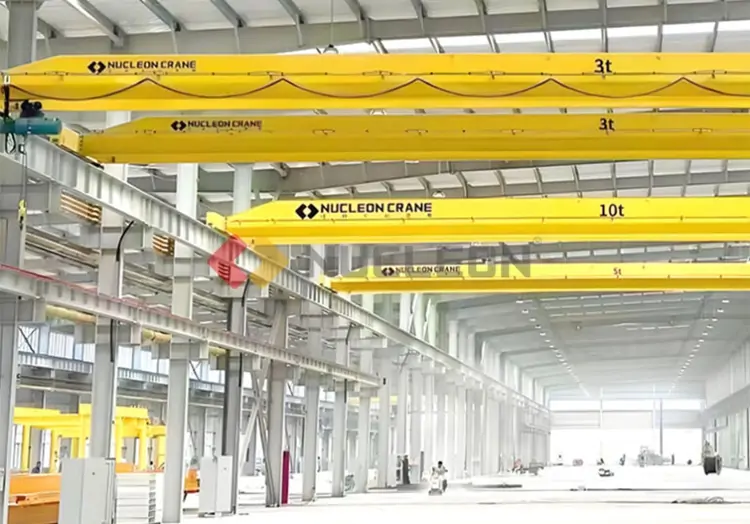

What is an Overhead Crane?
The overhead crane, also called an bridge crane or traveling crane, is a type of heavy-duty lifting equipment widely used in industry. Its name comes from its unique structural design: the ends of an overhead crane are supported on tall concrete columns or steel supports, and the overall shape resembles a bridge. These cranes are often used to efficiently lift materials across factories, workshops, warehouses or yards.
The overhead crane's bridge can run longitudinally along the tracks laid on the overheads on both sides, making full use of the space underneath the bridge for material handling, completely unimpeded by the equipment and space on the ground. Due to its large lifting capacity, flexible operability and wide range of application scenarios, the overhead bridge crane has become one of the most widely used and most numerous lifting equipments in the industrial field.
Overhead Crane Systems and Components
The overhead crane system mainly consists of components such as girders, rails, hoisting devices, trolleys, end girders, control devices and electrical power systems.
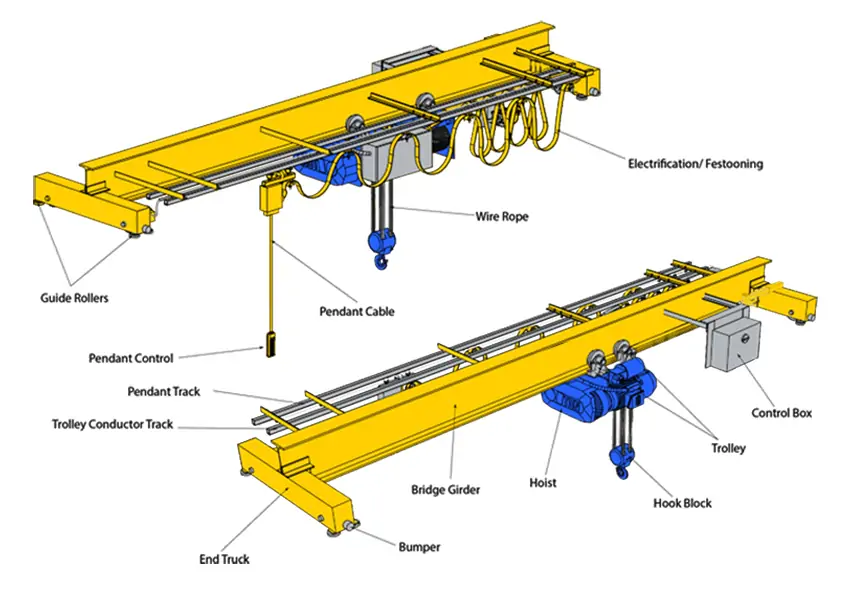
Introduction to Overhead Crane Parts
Girder
The girder is the main load-bearing structure of an overhead crane, spanning the entire width of the facility. It is responsible for supporting the hoisting device and the trolley, and determines the load carrying capacity and stability of the crane.
Track
The track is the basis for the operation of the overhead travelling crane and is usually laid on the overhead structure on both sides of the facility. The girder travelling mechanism moves longitudinally along the track, enabling the crane to operate flexibly over the entire working area.
Lifting device
The hoisting device is the core component of an overhead crane and is used to lift and lower loads. It usually consists of a motor, wire ropes, pulleys and hooks and is capable of precisely controlling the height and position of the load.
Trolley
Trolley is a mobile mechanism installed on the bridge frame, carrying the hoisting device and moving laterally along the beam. Through the operation of the trolley, the crane can precisely position the load within the range covered by the bridge.
End beams
The endcarriages are located at both ends of the girder and support the entire bridge structure and connect the girder traveling mechanism. The design of the endcarriages ensures that the crane is able to move smoothly along the track while bearing the weight of the load.
Control Unit
The system used to operate the crane, including hitch controls (hand controls), remote controls or cab controls.
Electrical power system
Provides power support for the crane, including motors, cables and power distribution units.
Types of Overhead Cranes
The overhead cranes can be divided into various types according to different lifting capacities, structures and application scenarios. Specifically as follows:
Divided by Lifting Capacity
1-20 tons light duty overhead travelling crane
Suitable for small manufacturing workshops, warehouses, etc., with a lifting capacity between 1 and 20 tons. Compact and flexible, they can efficiently handle small and medium-sized material handling tasks, making them ideal for use in light industrial environments.
Heavy duty overhead travelling crane over 20 tons
Mainly used in heavy industries such as steel mills, foundries, shipyards, etc., with a lifting capacity of more than 20 tons. Their sturdy structure and powerful lifting mechanism enable them to safely and stably handle extremely heavy loads and meet the demands of high-intensity operations.
Divided by Structural Design
Single Girder Overhead Crane
With single bridge design, supported by end trucks, it is suitable for 1-32 ton lifting needs. Its biggest advantage is its economic efficiency. It is widely used in manufacturing, logistics, automotive and other industries, and is especially suitable for the scenario of limited budget and moderate work intensity.
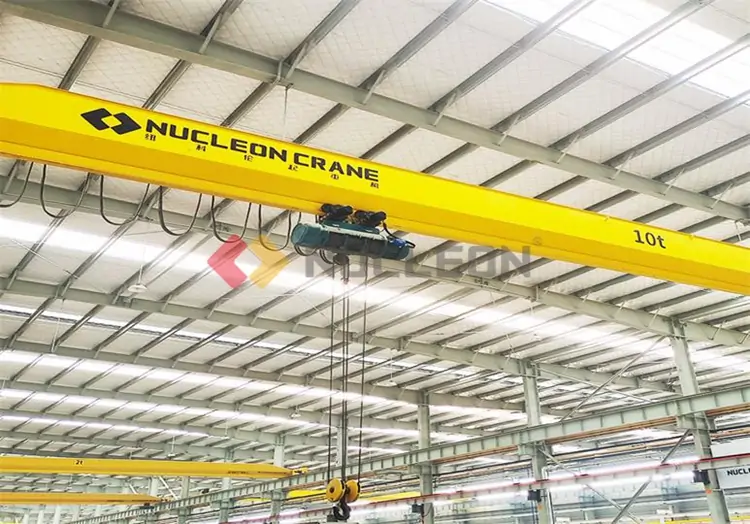

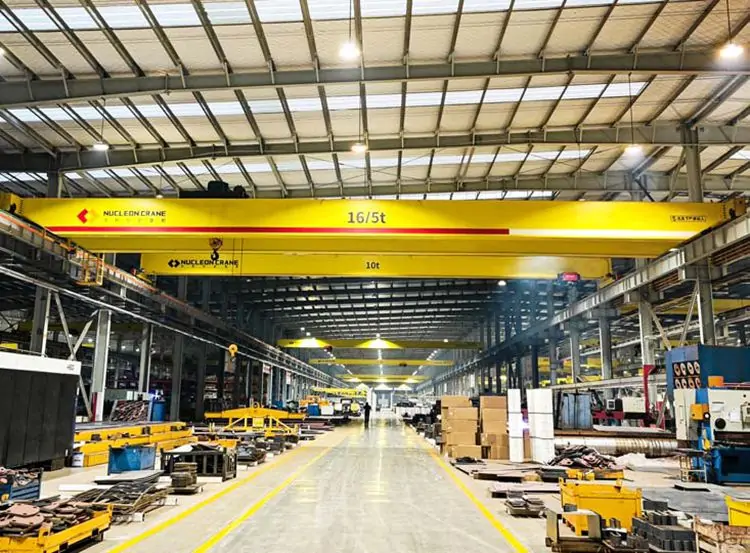
Double Girder Overhead Crane
Equipped with double bridge structure for greater stability, suitable for 5-800 ton large loads or large span operations. Commonly used in construction, mining and heavy manufacturing industries, they can efficiently handle complex and high-intensity lifting tasks.

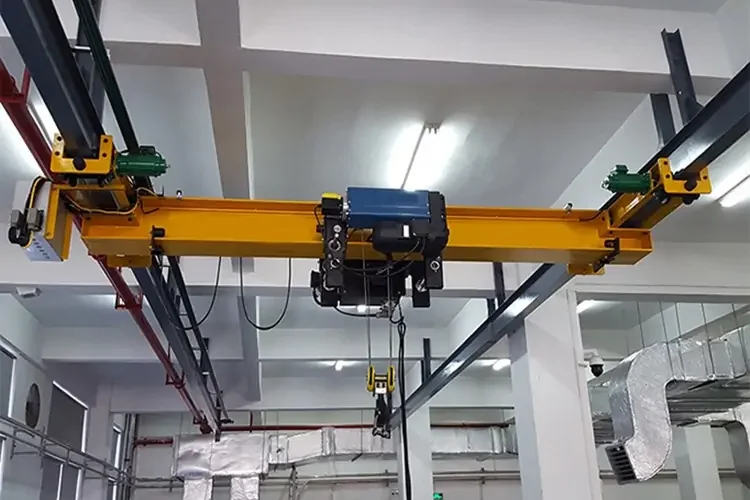
Underhung Overhead Cranes
Suspended from a ceiling structure to save floor space, they are suitable for workshops, assembly lines and storage areas where space is limited. Their flexible design is often used in locations where a free-standing crane cannot be installed.

Divided by Application
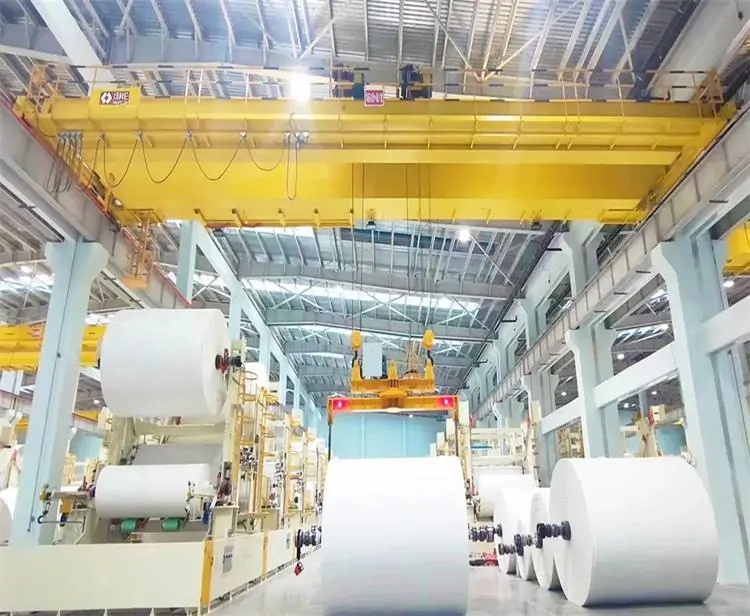
Paper Overhead Cranes
Designed for the paper industry, they are equipped with special attachments and lifting devices for efficient handling of paper rolls, pulp and other materials.

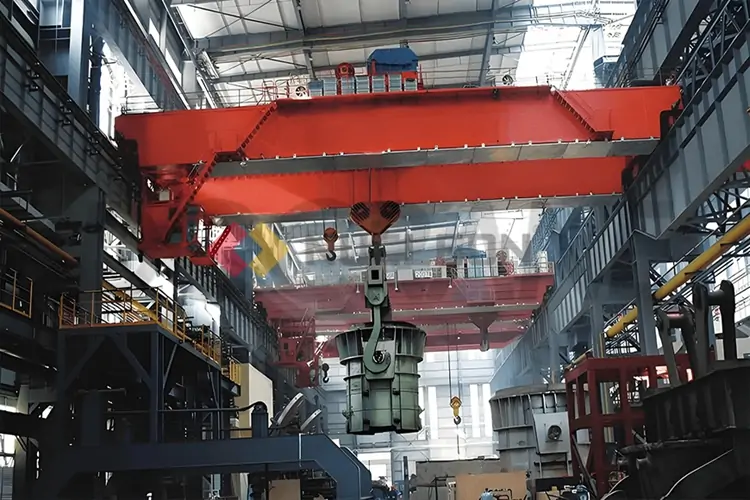
Ladle Overhead Cranes
Used in steel mills and foundries for conveying liquid metal, pouring and mixing molten iron during the smelting process, e.g. for lifting and conveying ladles of liquid steel. The use of heat-resistant materials and safe design allows for safe operation at extreme temperatures. Customized double and quadruple girder designs are available depending on lifting requirements.

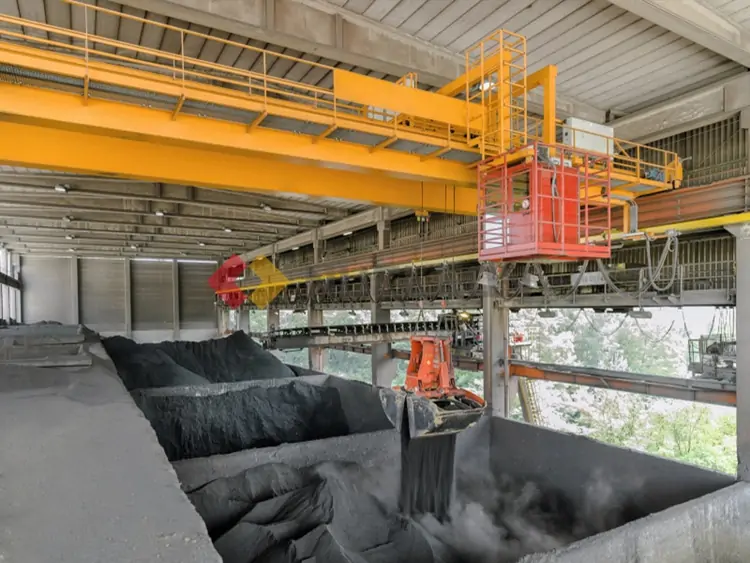
Grab Overhead Cranes
Equipped with a grapple attachment for handling bulk materials such as sand, gravel or waste. Widely used in the mining, construction and waste management industries to provide efficient loading and unloading solutions.

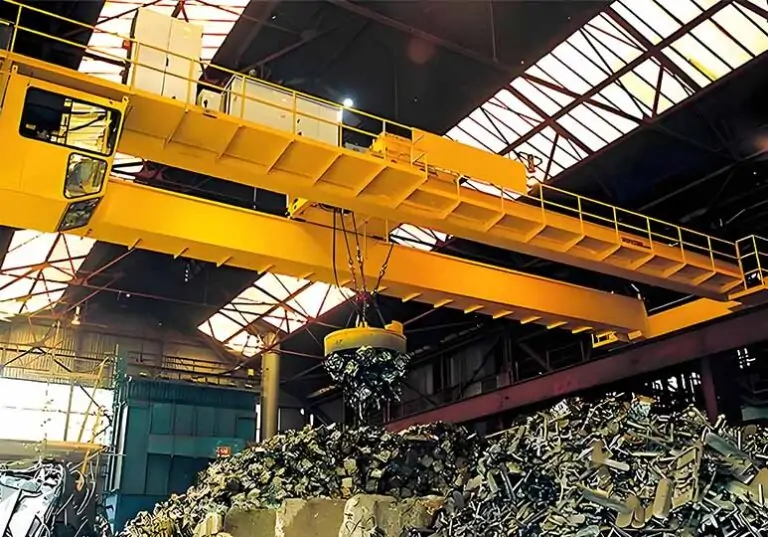
Electromagnetic Overhead Cranes
Uses electromagnetic force to move ferrous materials, commonly found in scrap yards, recycling centers and the steel industry. Their magnetic design allows for quick sorting and movement of metal materials, enhancing operational efficiency.

Explosion-Proof Overhead Cranes
Suitable for flammable and explosive environments, equipped with explosion-proof components and safety features to ensure safe operation in hazardous locations. Widely used in chemical and petroleum industries.
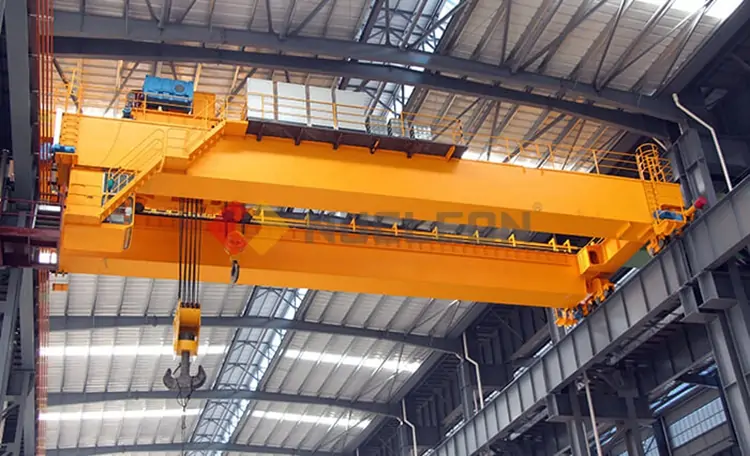

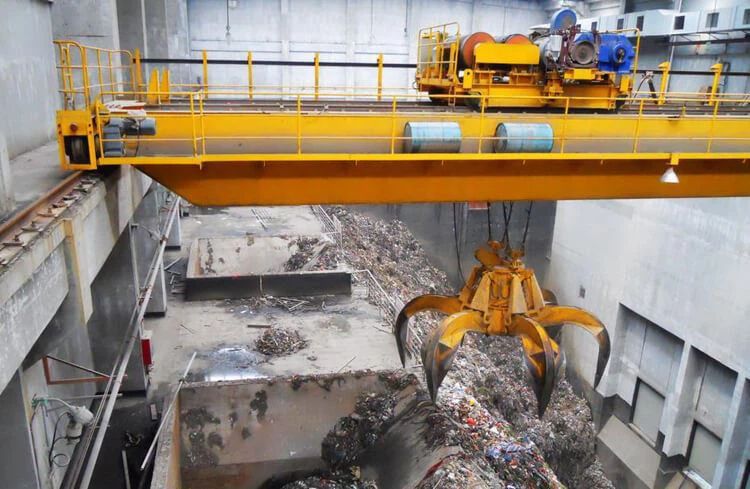
Energy Recovery Cranes
Tailor-made for the waste-to-energy (WtE) and biomass industries, equipped with special grabs, they can efficiently complete tasks such as handling, mixing, stacking, weighing and blending of waste materials. Typically in a twin configuration, two grab cranes of the same size are installed to work in tandem to ensure that the waste material enters the boiler uniformly to improve combustion efficiency.

How to Choose and Customize the Overhead Crane?
When selecting an overhead crane, the following key factors need to be carefully considered:
- load capacity:
First of all, define the maximum load capacity that the crane needs to handle, while reserving space for future business expansion. Ensure that the equipment will be able to cope with current and future work demands. - span range:
Span refers to the distance between crane rails or supports, which directly affects the coverage area of the equipment. According to the actual layout of the plant or work area, choose the appropriate span to ensure that the crane can efficiently cover the work area, while avoiding waste of space. - Lifting height:
Lifting height determines the operating range of the crane in the vertical direction. According to the height of the building and operational requirements, accurately calculate the required lifting height to ensure that there is sufficient headroom for material handling and to avoid conflict with the structure of the plant. - Operating environment:
Different operating environments have different requirements for crane performance. Need to consider the temperature, humidity, dust concentration and other factors, as well as industry-related safety regulations. For example, in flammable and explosive places, explosion-proof cranes should be selected to ensure safety. - Control system:
The crane's operating mode is also an important factor in the selection. Common control methods include pendant control, radio control and cab control. Choose the safest and most efficient control system according to the actual needs. - Maintenance and service:
When choosing a crane, you also need to consider its maintenance needs and the support of local services. Make sure that the supplier can provide timely technical support and maintenance services to ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment.
How to Choose a reliable overhead bridge crane supplier?
When choosing a overhead crane supplier, it is recommended to prioritize manufacturers with rich project experience who can provide high-quality products and services. Make sure the supplier has international quality standard certifications, such as ISO 9001 and CE certification. In addition, suppliers can be asked to provide reference cases from past customers to ensure that they have sufficient expertise in the design, manufacture and installation of overhead bridge cranes to ensure the safety, reliability and efficiency of the equipment.
How to operate an overhead crane?
- Pre-startup Inspection
Before operating the overhead crane, the operator must perform a thorough equipment inspection. First, make sure that the crane's power supply is connected properly and that the control panel has no abnormal display. Next, check whether there is any wear or damage to the wire rope, hook, pulley and other key components to ensure that they are in good condition. At the same time, check whether there are any obstacles on the track to ensure that the crane's running path is clear. Finally, test each control button and emergency stop device to ensure normal function. - Operation Procedure:
When operating the overhead crane, the operator should stand in the control room to ensure a clear view.
After starting the crane, carry out no-load test run first to make sure that the operation of the trolley, trolley and hoisting mechanism is smooth and without any abnormality.
When lifting cargo, the operator should start the hoisting mechanism slowly to avoid cargo shaking.
When moving the trolley or trolley, it is necessary to keep a constant speed and avoid stopping and starting sharply to prevent the goods from swinging or the crane from going out of control.
During the lifting process, the operator should always observe the status of the goods to ensure that the hook is firmly connected to the goods.
After completing the lifting, park the crane in the designated position, turn off the power and make daily maintenance records.
How to maintain the overhead travelling crane?
- Daily Maintenance
Daily maintenance of overhead cranes is the key to ensure their long-term stable operation. At the end of each day's work, the operator should clean the dust and debris on the surface of the crane, especially the rail and pulley parts, to prevent the accumulation of dust from affecting the operation. At the same time, check the wire ropes for broken wires, deformation or wear, and lubricate or replace them if necessary. For the electrical system, check cables and terminals regularly to ensure there is no looseness or aging. In addition, operators should regularly test limit switches and emergency stops to ensure sensitivity and reliability. - Regular Maintenance
In addition to routine maintenance, overhead cranes require regular professional maintenance. Every three months or according to the frequency of use, the mechanical parts of the crane should be fully lubricated, including bearings, gears and chains, etc., in order to reduce wear and noise. Every six months, the structure of the crane needs to be inspected in detail by professional technicians, especially whether there are any cracks or deformations in the welds of the main girder, end girder and outriggers. For the electrical system, a comprehensive inspection should be carried out once a year, including the performance test of motors, controllers and sensors, to ensure that they meet the safety standards. Regular maintenance not only extends the service life of the crane, but also effectively prevents sudden breakdowns and ensures operational safety.
Summarize:
Above is about the types, components and operation and maintenance of overhead cranes. There are many types of overhead cranes for different industries and operating environments. Whether it's a small, light-duty shop or a large, heavy-duty industrial site, each type of crane has its own unique features and benefits. By understanding the features and usage scenarios of each crane, you can make a more correct choice of lifting solution.
For customized overhead crane solutions, please feel free to Kontaktieren Sie uns. Our professional team will provide you with personalized advice and help you choose the most suitable equipment.
Verwandte Artikel
- Unterschiede zwischen Einträger- und Zweiträger-Brückenkranen
- Was ist ein Brückenkran? Definition, Teile, Typen, Verwendung, Kosten
- Vergleich zwischen Brückenkran und Portalkran: Wie wähle ich?
- Einführung in MG Box Frame Gantry Crane
- LD-Einträger-Brückenkran
- CD1, MD1 Elektrohebezeug Kurze Einführung






