When lifting heavy objects, choosing the right hoist is crucial. Manual chain hoist and electric chain hois are two common choices, and they each offer unique advantages and scenarios for application. Understanding the differences between manual and electric chain hoists can help you make the best choice for your actual needs. In this article, we'll analyze the features, operation, load capacity, application scenarios, and maintenance points of these two types of Chain Hoists to help you find the best lifting solution for your needs.
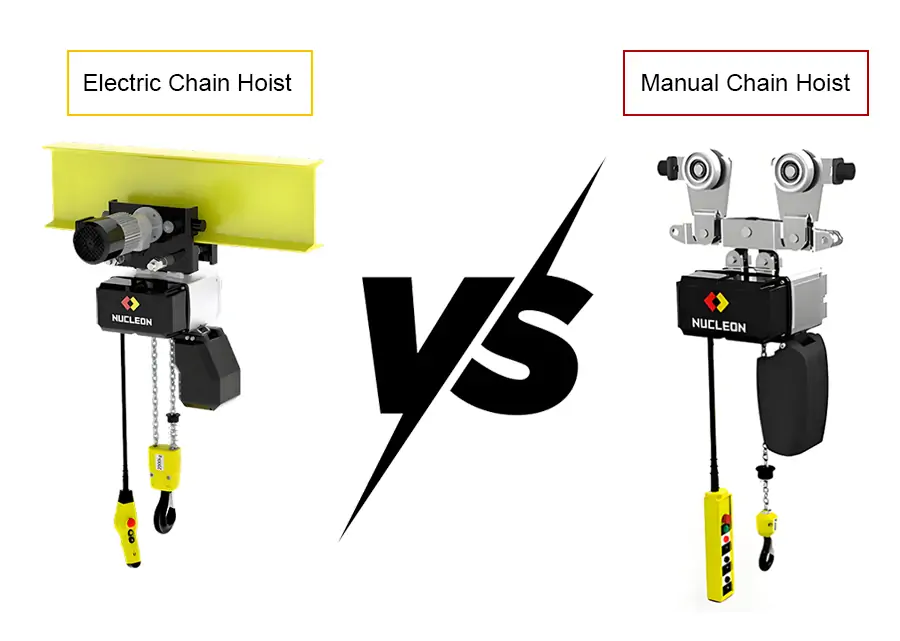
What are Manual and Electric Chain Hoists?
A manual chain hoist, also known as a hand chain hoist, is a mechanical device that relies on human power to operate. It lifts or lowers loads by means of a chain and pulley system. Manual chain hoists are known for their simplicity, portability and the fact that they require no external power source. Since its operation relies on human power, it is suitable for occasions with lighter loads and less frequent use, such as small workshops, maintenance work or temporary lifting tasks.
Electric chain hoists are motor-driven lifting devices designed for heavy lifting operations with frequent use and are widely used in industrial environments. Compared to manual chain hoists, electric chain hoists offer higher operating speeds, greater load capacity and easier operation, which can significantly improve work efficiency. However, electric chain hoists have a higher initial acquisition cost and require a stable power supply, making them more suitable for applications that require efficient, continuous operation, such as factories, warehouses or large construction sites.
How to operate a manual chain hoist and an electric chain hoist?
Manual chain hoists rely entirely on human power to operate the process, with the user pulling a hand chain to drive an internal gear system to raise or lower the load, which is usually less efficient than electric hoists.
Electric chain hoist operation is mainly through the control handle or remote control, the user can easily start the motor to drive the lifting mechanism, to achieve the smooth lifting and lowering of the load. Electric chain hoists operate faster, more accurately, and require little physical effort.
Load capacity of Manual and Electric Chain Hoists
Manual chain hoists generally have low load capacities, usually between 0.5 and 20 tons. It relies on manual operation to accomplish lifting tasks and is suitable for lighter loads and lifting operations that do not require automation.
Electric chain hoists can handle heavier loads and are often used in conjunction with overhead cranes with load capacities of 0.25 to 32 tons or more. They are ideal for frequent and heavy lifting tasks.
Applications
Manual chain hoists are usually used in conjunction with beam trolleys or monorail trolleys. Suitable for small workshops, garages, construction sites and areas without electricity supply.
Electric chain Hoists Usually used in combination with overhead cranes, gantry cranes or jib cranes. Ideal for factories, warehouses, manufacturing plants and any place where heavy loads need to be lifted frequently.
Price comparison of manual and electric chain hoists
There are significant cost differences between manual and electric chain hoists, mainly in terms of initial investment and long-term maintenance costs.
Electric chain hoists typically require a higher initial investment, largely attributable to their complex electrical components and advanced features such as overload protection, limit switches, and automated control systems. Additionally, electric hoists have higher ongoing maintenance costs, including electrical inspections, component maintenance, and potential motor repair costs. These factors increase the total cost of ownership of electric hoists over time.
In contrast, manual chain hoists have lower up-front and maintenance costs. Because of their simple construction and lack of electrical components, manual chain hoists have a more economical initial purchase price and require little additional electrical inspection or complex maintenance. This low-cost feature makes it ideal for small jobs, workshops or budget-constrained scenarios.
While manual chain hoists may not be as good as electric hoists in terms of load capacity and operating speed, their overall cost advantage makes them more attractive in situations where automation or advanced features are not required.
Price Range:
Manual chain hoists: Prices typically range from $100 to $1,000, depending on load capacity and brand.
Electric chain hoists: A wider range of prices, typically $500 to $5,000 or more, depending on load capacity, feature set, and brand.
How to choose between manual or electric chain hoists?
When choosing between a manual chain hoist and an electric hoist, you need to make a comprehensive assessment of the three aspects of efficiency, portability and power requirements according to your specific needs.
1. Efficiency comparison: which chain hoist is faster and more efficient?
Electric chain motive manufacturing assembly line, electric hoists can quickly lift and position heavy components to enhance productivity.
In contrast, manual chain hoists are more suitable for lighter loads and less frequent use due to their reliance on manual labor and slower operating speeds. Despite their lower efficiency, manual hoists offer unique advantages in scenarios that require delicate maneuvers or space constraints. For example, when removing equipment or performing precision installations in confined spaces, manual hoists offer greater operational flexibility and control accuracy.
2. Portability comparison: Which chain hoist is easier to move and install?
Electric chain hoists are typically heavier and require fixed installations or specific support systems, making them less portable. Their complex electrical components and heavy-duty design make them more suitable for industrial environments with permanent or semi-permanent installations, such as factory floors or warehouses.
Manual chain hoists are simple, lightweight, flexible, portable and require no power source. As a result, manual hoists can be easily transported and quickly deployed to a variety of work areas. It is widely used in workshop maintenance, temporary operations, and remote areas with limited power supply, making it ideal for scenarios where mobility and flexibility are important.
3. Power requirements: does it need power support?
Electric chain hoists need to run on power, so their use in remote areas with unstable power supply or no access to power will be limited. Manual chain hoists, on the other hand, require no power support at all and can be operated solely by human power. They are suitable for use in areas where electricity is not available or unreliable, such as outdoor construction sites or temporary work sites.
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages
Manual Chain Hoists:
- Pros: Affordable, portable, no power source required, easy to maintain.
- Cons: Slower running speed, limited load capacity, requires physical strength.
Electric Chain Hoists:
- Pros: High efficiency, can carry heavy loads, low physical effort.
- Disadvantages: higher cost, need power supply, maintenance is more complicated.
Safety Functions of Manual and Electric Hoists
Manual Hoists
- Mechanical brake: locks automatically when operation is stopped, preventing the load from slipping accidentally.
- Load limiting device: prevents overloaded operation, protects equipment from damage and ensures personnel safety.
- High-strength chain: Made of high-quality alloy steel, resistant to abrasion and breakage, enhancing overall safety.
- Manual control: the operating speed is directly controlled by the user, suitable for fine work and reducing the risk of accidents.
Electric hoist:
- Overload protection system: automatically detects overload and stops operation to protect equipment and personnel safety.
- Emergency stop button: one key stop function to cope with unexpected situation.
- Fail-safe brake: automatically locks in case of power failure or malfunction to prevent the load from falling.
- Limit switch: Prevents the hoist from running beyond the safe range to avoid collision or damage.
- Electrical protection: Built-in short-circuit protection and overheating protection to ensure safe operation of the motor.
How To Maintain Manual And Electric Hoists?
Regular maintenance is the key to ensuring the safe operation and long service life of your hoist. Here are the key points of maintenance for manual hoists and electric hoists:
Manual Hoist Maintenance:
- Chain Inspection: Regularly inspect the chain for wear, cracks or deformation. Clean and lubricate the chain to prevent rust and jamming.
- Gear and Pulley System: Check gears and pulleys for proper engagement to ensure smooth operation. Remove dust and debris to avoid affecting performance.
- Brake Testing: Test mechanical brakes for proper operation to ensure they are effective in locking loads.
- Load Limiter: Check whether the load limiting device is sensitive to prevent overload operation.
- Exterior Inspection: Check whether the shell and connecting parts are damaged or loose, and repair or replace them in time.
Electric Hoist Maintenance:
- Electrical system check: Regularly inspect motor, cables and control handle to ensure no damage or deterioration. Test the emergency stop button and limit switches for proper operation.
- Brake and Overload Protection: Check fail-safe brakes and overload protection systems to ensure they are sensitive and reliable.
- Chain or Wire Rope Maintenance: Check the chain or wire rope for wear, breakage or deformation. Clean and lubricate to ensure smooth operation.
- Mechanical Component Lubrication: Regularly lubricate gears, bearings and pulleys to reduce friction and wear.
- Running Tests: Conduct regular no-load and load tests to check for smooth operation and no abnormal noise.
- Environmental cleanliness: Keep the hoist and its surroundings clean to prevent dust and debris from affecting performance.
General Maintenance Recommendations:
- Follow the maintenance manuals and operating instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- Perform regular professional inspections, especially on frequently used hoists.
- Keep a maintenance log to track equipment status and repair history.
Conclusion
In summary, when choosing manual hoist or electric hoist, you need to consider the load capacity, operating efficiency, operational portability and other factors according to the specific needs and application scenarios. If you need efficient, frequent lifting operations, and the working environment of adequate power, electric hoist is a better choice. If the work scenario is variable, the load is light, or the power supply is limited, a manual hoist is more cost-effective and practical.
If you still have questions, feel free to contact the Nucleon Crane team for expert advice and solutions.







